The Role of Blood Clots in the Body
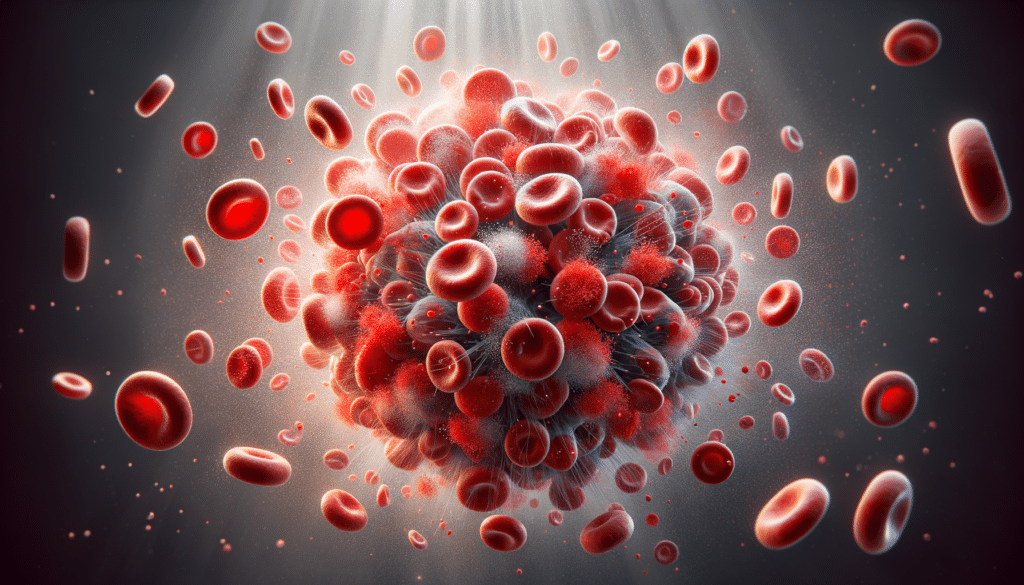
Blood clots are often misunderstood as purely harmful, yet they play a vital role in our body’s defense mechanism. When an injury occurs, the body initiates a complex process known as coagulation to prevent excessive bleeding. This involves the transformation of liquid blood into a gel-like state, effectively sealing wounds and facilitating healing. Without this natural response, even minor injuries could result in significant blood loss, highlighting the importance of clots in maintaining our health.
However, the formation of blood clots is a delicate balance. On one hand, they are essential for survival; on the other, they can become life-threatening if they form unnecessarily or do not dissolve after healing. Understanding this dual nature is key to addressing both the protective and potentially harmful aspects of blood clots.
Key points to consider:
- Blood clots are crucial for stopping bleeding and starting the healing process.
- They form through a process called coagulation, involving platelets and proteins.
- While essential, clots can become dangerous if they occur inappropriately within blood vessels.
Causes and Risk Factors of Blood Clots
Blood clots can occur due to various factors, ranging from genetic predispositions to lifestyle choices. One of the primary causes is immobility, which can lead to conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Prolonged periods of inactivity, such as long flights or bed rest, can cause blood to pool and clot in the veins.
Other risk factors include smoking, obesity, and certain medications, all of which can increase the likelihood of clot formation. Additionally, individuals with a family history of clotting disorders may be at a higher risk, as genetic factors can influence the body’s coagulation processes.
Pregnancy and certain medical conditions, such as cancer and heart disease, also contribute to the risk. Understanding these causes and risk factors is crucial for prevention and management, as early detection can significantly reduce the potential for serious complications.
Important risk factors include:
- Prolonged immobility, such as during long travel or hospitalization.
- Lifestyle choices like smoking and obesity.
- Genetic predispositions and family history of clotting disorders.
- Medical conditions like cancer, heart disease, and pregnancy.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Blood Clots
Recognizing the symptoms of blood clots is essential for timely intervention. Common signs include swelling, pain, and redness in the affected area, often seen in cases of DVT. In more severe instances, clots can travel to the lungs, causing a potentially fatal condition known as pulmonary embolism, characterized by sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing up blood.
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of physical examinations, imaging tests such as ultrasounds, and blood tests to measure clotting factors. Early diagnosis is critical to prevent complications, emphasizing the need for awareness and prompt medical attention when symptoms arise.
Key symptoms to watch for:
- Swelling, pain, and redness, particularly in the legs.
- Sudden shortness of breath and chest pain.
- Coughing up blood, indicating possible pulmonary embolism.
Treatment and Prevention of Blood Clots
Treatment for blood clots often involves anticoagulant medications, which help to prevent further clotting and allow the body to dissolve existing clots. In some cases, thrombolytic therapy may be used to break down clots more rapidly, though this is typically reserved for severe cases due to the risk of bleeding.
Prevention strategies are equally important and include lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking. For those at higher risk, medical interventions like compression stockings and blood thinners may be recommended to reduce the likelihood of clot formation.
Effective prevention and treatment strategies include:
- Use of anticoagulant medications to prevent further clotting.
- Lifestyle changes like exercise and weight management.
- Medical interventions such as compression stockings and blood thinners for high-risk individuals.
The Future of Blood Clot Management
Advancements in medical research continue to enhance our understanding and management of blood clots. Innovative treatments, such as targeted therapies and personalized medicine, are being developed to improve outcomes and reduce side effects. Additionally, technology plays a crucial role, with wearable devices and apps providing real-time monitoring of individuals at risk, offering new avenues for prevention and early intervention.
As our knowledge grows, the future of blood clot management looks promising, with the potential for more effective and individualized approaches. Continued research and technological integration are key to tackling the challenges posed by blood clots and improving patient care.
Future directions in blood clot management:
- Development of targeted therapies and personalized medicine.
- Use of wearable technology for real-time monitoring and prevention.
- Ongoing research to enhance understanding and treatment options.